Viral Hepatitis
What is Viral Hepatitis?
Viral hepatitis is an infection that causes inflammation of the liver. The liver is a vital organ that helps filter toxins from your blood, process nutrients, and support digestion.
There are several types of viral hepatitis, but the most common in the United States are Hepatitis A, B, and C. Other types exist worldwide but are less common in the U.S.
Untreated hepatitis can lead to serious problems such as liver scarring (cirrhosis), liver failure, or liver cancer.
-
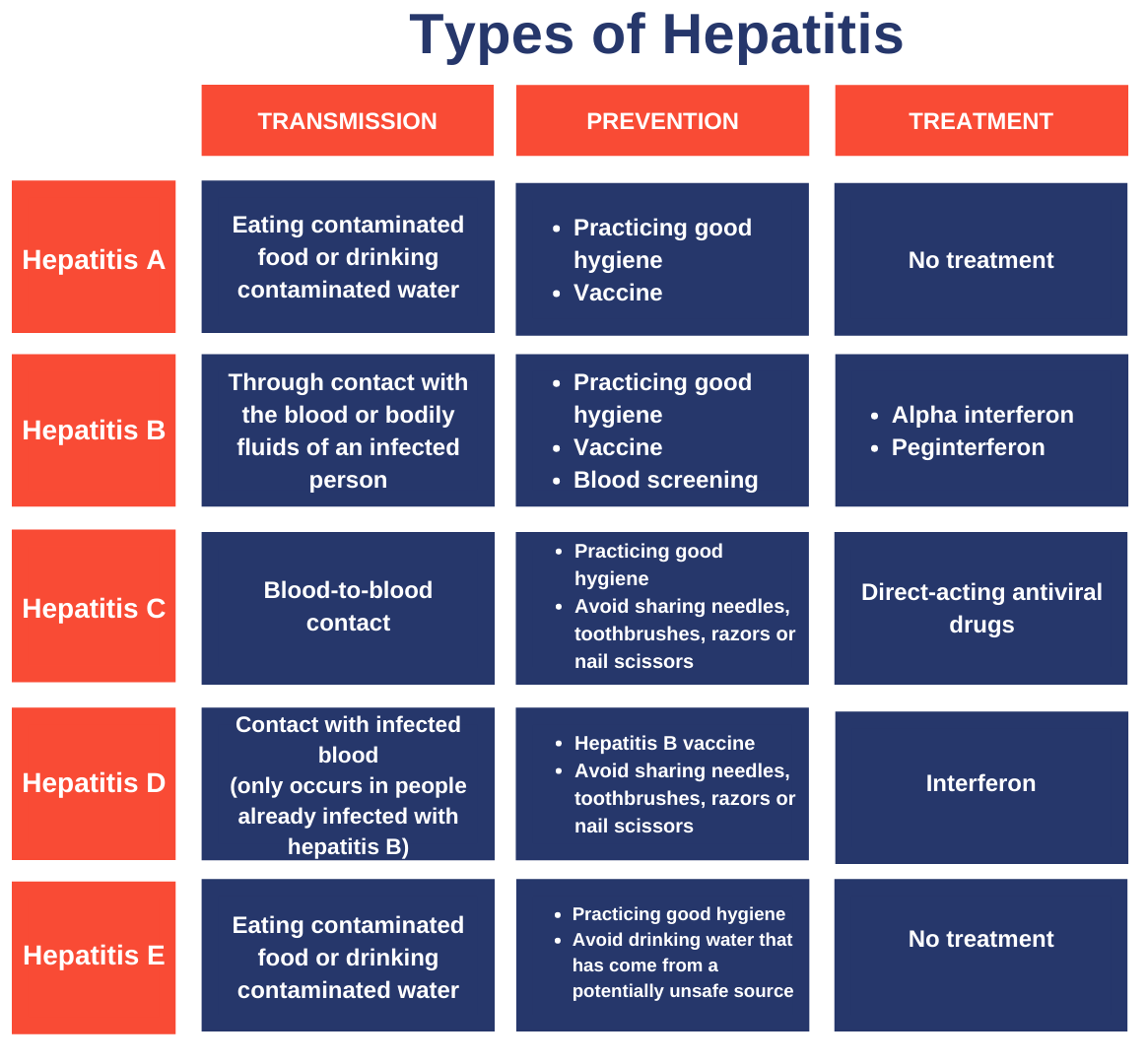
How it spreads: Mainly through contaminated food or water, or close contact with someone who is infected.
Symptoms: Fatigue, nausea, stomach pain, dark urine, and yellowing of the skin or eyes (jaundice).
What to know: Usually short-term and mild. Most people recover completely. Long-term liver damage is rare.
-
How it spreads: Through blood, semen, or other bodily fluids. This can happen during sex, sharing needles, or from mother to baby at birth.
Symptoms: Many people have no symptoms at first. Some may feel tired, nauseated, or notice jaundice and joint pain.
What to know: Hepatitis B can become chronic in some people. Chronic infection can lead to liver scarring, liver failure, or liver cancer.
-
How it spreads: Mainly through blood-to-blood contact. Sharing needles is the most common way it spreads. Sexual transmission is less common.
Symptoms: Often there are no symptoms for many years. Some people may feel tired, notice jaundice, or have stomach discomfort.
What to know: Hepatitis C often becomes chronic. Untreated chronic infection can cause liver scarring, liver failure, or liver cancer.
-
How it spreads: Only occurs in people who are already infected with Hepatitis B. Spread through blood or bodily fluids.
Symptoms: Similar to Hepatitis B. Can make HBV infection more severe.
What to know: Preventing Hepatitis B with vaccination also prevents Hepatitis D.
-
How it spreads: Usually through contaminated water in countries with poor sanitation. Rare in the United States.
Symptoms: Fatigue, nausea, jaundice, and abdominal pain. Often mild and short-term.
What to know: Usually resolves on its own. Pregnant people are at higher risk for severe illness.
Types of Hepatitis
Prevention Options
Hepatitis A and B can be prevented with safe and effective vaccines.
Practicing safe sex and never sharing needles lowers your risk for Hepatitis B and C.
There is no vaccine for Hepatitis C, so avoiding blood-to-blood contact is the best protection.
Using safe water and good food hygiene, especially when traveling, can help prevent other less common types of hepatitis.
In general, not sharing personal items that may carry blood, like razors or toothbrushes, reduces the chance of infection.
How Can I Get Tested for Viral Hepatitis?
If you are concerned about hepatitis or want reassurance about your status, please visit our testing services page or talk with your provider about testing options.
To learn more about viral hepatitis, click here.